HomeBlogBasic Electrical EngineeringSolved Problems on Superpositi...
1) Find Current flowing through 1 \Omega resistor by using superposition theorem.


Consider 130 V Voltage source only.
-0.2I_1-0.2(I_1-I_2)+130 = 0
-0.4I_1 +0.2I_2 = -130 \ldots\ldots (1)
-I_1-0.2(I_2-I_1)-0.2I_2=0
0.2I_1-1.4I_2=0 \ldots\ldots (2)
I_1 = 350 A
I_2 = 50 A
I’_{1\Omega} = 50 A (\downarrow)

Consider 110 V only.
-0.2I_1 -0.2(I_1-I_2)-110 = 0
-0.4I_1+0.2I_2 = 110 \ldots\ldots(3)
-I_2+110-0.2(I_2-I_1)-0.2I_2=0
0.2I_1 – 1.4I_2 = -110 \ldots\ldots (4)
I_1 = -253.8467 A
I_2 = 42.3076 A
I’’_{1\Omega} = 42.3076 A (\downarrow)
\therefore I_{1\Omega} = I’_{1\Omega} + I’’_{1\Omega} = 50 + 42.3076 = 92.3076 A (\downarrow)
2) Find current flowing through 5 \Omega .
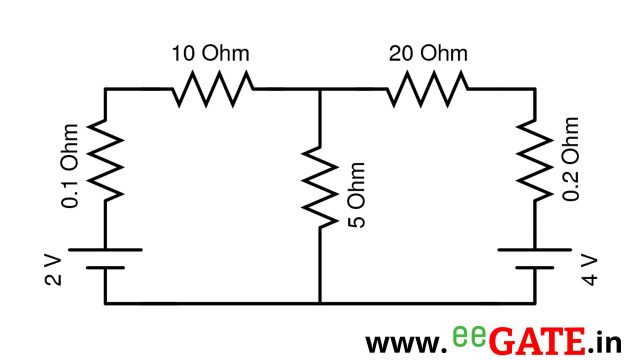

2-0.1I_1-10I_1-5(I_1-I_2)=0
15.1I_1 + 5I_2=-2 \ldots\ldots (1)
-20I_1-0.2I_2-5(I_2-I_1)=0
5I_1-25.2I_2=0 \ldots\ldots (2)
I_1 = 0.1417 A
I_2 = 0.02812 A
I’_{5\Omega} = I_1-I_2 = 0.1158 A (\downarrow)

Consider 4 V only.
-0.1I_1-10I_1-5(I_1-I_2) = 0
-15.1I_1+5I_2 = 0 \ldots\ldots (3)
20I_2-0.2I_2-4-5(I_2-I_1)=0
5I_1-25.2I_2 = 4 \ldots\ldots (4)
I_1 = -0.05685 A
I_2 = -0.1698 A
I’’_{5 \Omega} = I_2-I_1 = 0.1130 A (\downarrow)
I_{5 \Omega} = I’_{5\Omega} + I’’_{5\Omega} = 0.2288 A (\downarrow)
3) Determine current through 1 \Omega resistor.


Consider a 10 V voltage source only.
-2(I_1-I_2)-2I_1 = 0
-4I_1+2I_2=0 \ldots\ldots (1)
-10 -2(I_2-I_1)-I_2=0
2I_1-3I_2=10 \ldots\ldots (2)
I_1 = -2.5 A
I_2 =-5 A
I’_{1\Omega} = -5 A (\rightarrow)

Consider a 6 V voltage source only.
-2I_1-2(I_1-I_2)-6 = 0
-4I_1+2I_2=6 \ldots\ldots (3)
-I_2+6-2(I_2-I_1)=0
2I_1 – 3I_2 =-6 \ldots\ldots (4)
I_1 = -0.75 A
I_2 =1.5 A
I’’_{1\Omega} = 1.5 A (\rightarrow)

Consider 8 V only.
8-2I_1-2(I_1-I_2)=0
-4I_1+2I_2=-8 \ldots\ldots (5)
-I_2-2(I_2-I_1)=0
2I_1-3I_2=0 \ldots\ldots (6)
I_1 = 3 A
I_2 = 2 A
I’”_{1\Omega} = 2 A (\rightarrow)
Total \; \; current \; \; I_{1 \Omega}=I’_{1 \Omega}+I’’_{1 \Omega}+I’’’_{1 \Omega}
I_{1 \Omega}= 2+1.5+(-5) = -1.5 A (\rightarrow)
I_{1 \Omega} = 1.5 A (\leftarrow)
4) Find current through 20 \Omega resistor.


For Mesh 1:
10-10I_1+10I_2=0
-10I_1+10I_2=-10 \ldots \ldots(1)
For Mesh 2:
-10I_2+10I_1-I_2-20I_2=0
10I_1-31I_2=0 \ldots\ldots(2)
I_1 = 1.4761 A
I_2 = 0.4761 A
I’_{20\Omega} = 0.4761 A (\downarrow)

Consider 8 V voltage source only.
-I-8-20I=0
-21I = 8
I’’_{20\Omega} = -0.3809 A (\downarrow)

Consider a 12 V voltage source only.
-12-8I_1+8I_2=0
-8I_1+8I_2=12 \ldots\ldots(3)
-I_2-8I_2+8I_1-20I_2=0
8I_1-29I_2=0 \ldots\ldots(4)
I_1=-2.0714 A
I_2=-0.5714 A
I’’’_{20\Omega} = -0.5714 (\downarrow)
I_{20\Omega} = I’_{20\Omega}+I’’_{20\Omega}+I’’’_{20\Omega}
I_{20\Omega} = 0.4761+(-0.3809)+(-0.5714)
I_{20\Omega} = -0.4762 A (\downarrow)
I_{20\Omega} = 0.4762 A (\uparrow)


Add a Comment